Circuitry and Brain-Body Interactions | 2021
Role of Enteroendocrine Cells in the Origin of Parkinson’s Pathology
Study Rationale: Emerging evidence supports the concept that alpha-synuclein pathology, a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD), might originate in the gastrointestinal tract and spread to the brain. However, where and how pathological alpha-synuclein initially forms remains unclear. Certain gut microbiota and some environmental toxins have been associated with PD. Team Liddle recently discovered that specialized sensory cells in the gut known as enteroendocrine cells (EECs), in direct contact with gut microbiota and different environmental toxins, might transfer misfolded alpha-synuclein to the nervous system in disease.
Hypothesis: Team Liddle hypothesizes that gut microbes and environmental toxins, alone or in combination, corrupt alpha-synuclein protein expressed in EECs to misfolded pathological forms that might spread to the nervous system in a novel circuit important in PD.
Study Design: Using a unique, large, and well-characterized collection of human data, Team Liddle will identify potential triggers and alterations in gut microbiota and neuroinflammatory pathways that are associated with PD. The team will test known and experimental triggers (toxins and microorganisms) in two complementary model systems (ex vivo cultures, and in vivo in mice) to determine effects on the formation and spread of pathological alpha-synuclein within a predictable circuit of interconnected cells vulnerable to disease.
Impact on Diagnosis: These studies will (a) establish how EECs are involved in the formation of pathological alpha-synuclein at the earliest stages of disease, (b) identify gut-associated toxins and microbes that contribute to PD, (c) develop novel “humanized” pre-clinical model systems, and (d) test two particularly promising experimental therapeutic approaches in the novel model systems.
Leadership
Project Outcomes
Team Liddle's project will characterize specialized sensory cells of the gut, known as enteroendocrine cells, as a target for Parkinson’s disease-associated toxicant, gut microbiome, and immune interactions leading to alpha-synuclein pathology, and as a conduit to vagal, enteric, and spinal neurons. View Team Outcomes.
Team Outputs
Click the following icons to learn more about the team’s outputs:
Overall Contributions
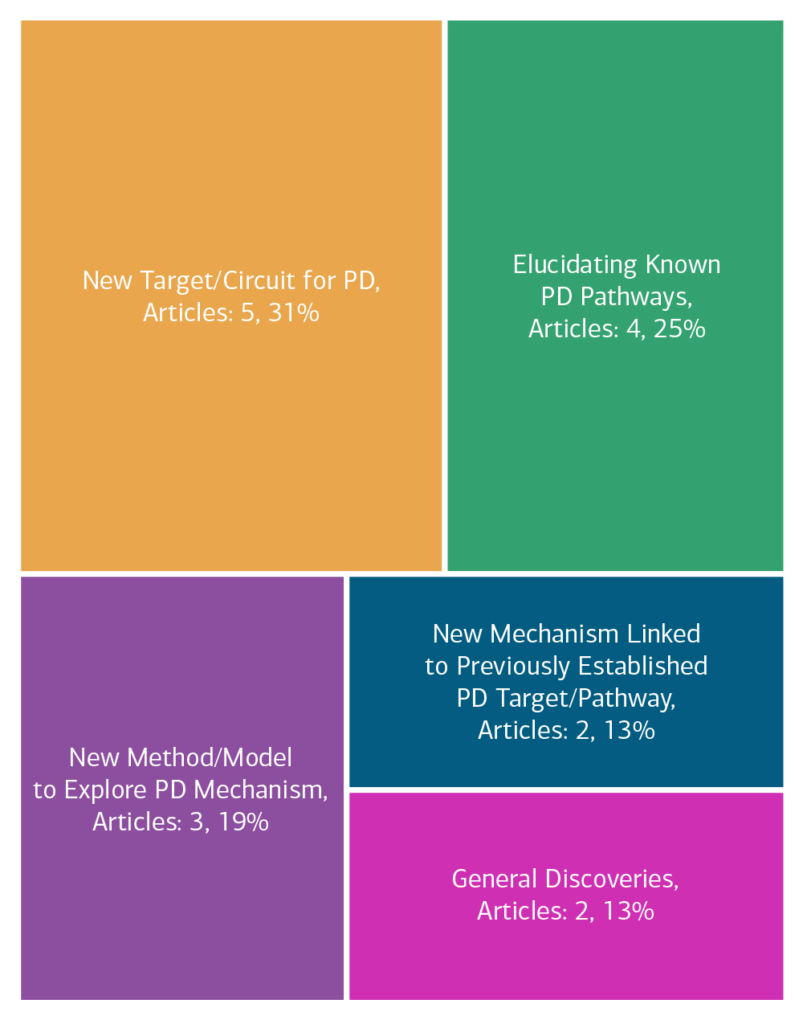
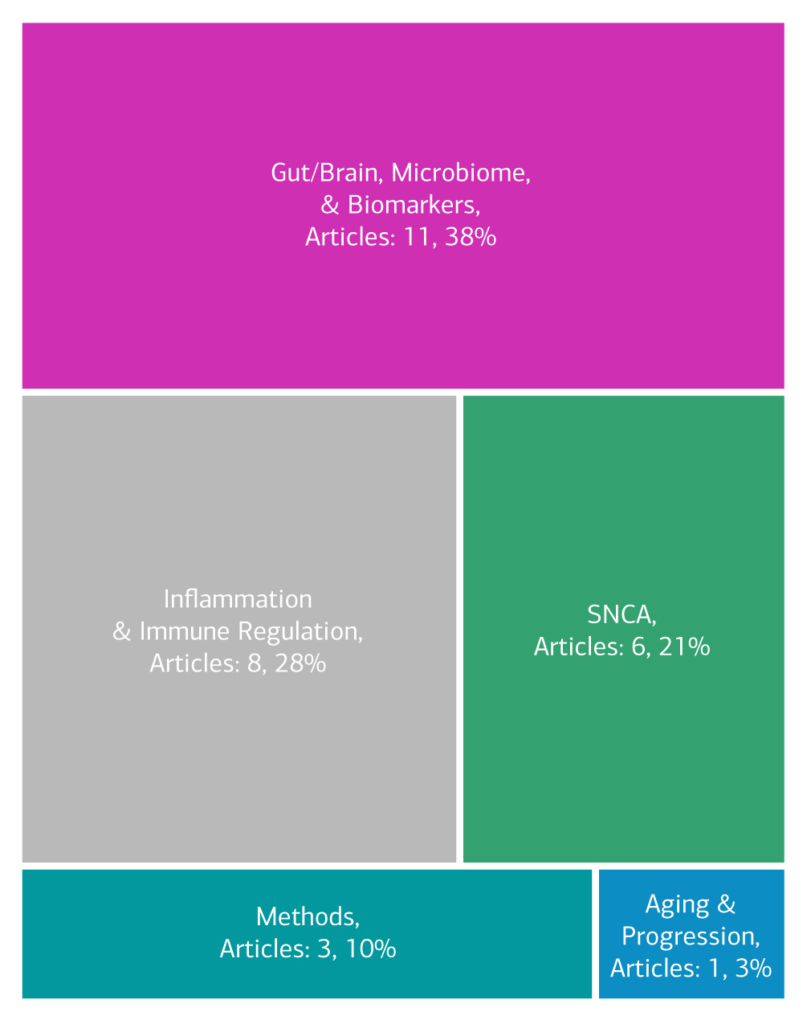
Here is an overview of how this team’s article findings have contributed to the PD field as of May 2025. There are two different categorizations of these contributions – one by impact to the PD community and a second by scientific category.
Impact
Category
Featured Output
Below is an example of a research output from the team that contributes to the ASAP mission of accelerating discoveries for PD.
The pyrethroid insecticide deltamethrin disrupts neuropeptide and monoamine signaling pathways in the gastrointestinal tract
This research reveals how pyrethroids (common insecticides) impact specialized intestinal enteroendocrine cells (EECs), which function similarly to neurons. The study demonstrates that deltamethrin (a pyrethroid) directly affects serotonin pathways and inhibits hormone release in cultured EECs. In mice given oral exposure, deltamethrin caused temporary intestinal motility issues (constipation), reduced peripheral serotonin, and suppressed nutrient-stimulated hormone release (including GLP-1, insulin, and leptin). These findings establish EECs as vulnerable to pyrethroid toxicity and provide a mechanistic link between pyrethroid exposure and various associated conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders (IBS, IBD), metabolic disruptions (diabetes), and potentially even neurological conditions with GI symptoms like Parkinson’s disease.
Team Accolades
Members of the team have been recognized for their contributions.
- Open Science Champions: Haydeh Payami, Rodger Liddle
- Network Spotlights: Haydeh Payami

Other Team Activities
-
Working Groups: Microbiome – Haydeh Payami (Co-Chair)
- Interest Groups: Gut/Brain, Microbiome, and Clinical Biomarkers – Haydeh Payami (Co-Chair)
In the News
- Duke-led teams awarded $18 million to investigate Parkinson’s disease (Duke Neurobiology, October 29, 2021)
- Grants support researching role of non-neuronal cell types (Parkinson’s News Today, October 29, 2021)
- Metagenomics of Parkinson disease implicates the gut microbiome in multiple disease mechanisms (Neurology Podcast, December 15, 2022)
- New study puts gut microbiome at the center of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis (Science Daily, January 10, 2023)
- Nanoplastics promote conditions for Parkinson’s across various lab models (Duke Health, November 17, 2023)
- Tiny pieces of discarded plastics like styrofoam may promote Parkinson’s (Parkinson’s News Today, December 6, 2023)
- A substantial number of Parkinson’s disease cases can be attributed to preventable risk factors, new research finds (The University of Alabama, December 14, 2023)
- Favre’s Parkinson’s disease diagnosis raises questions about link to football; UAB research might have answers (WBRC, September 26, 2024)